Side Man Body Drawing Muscle
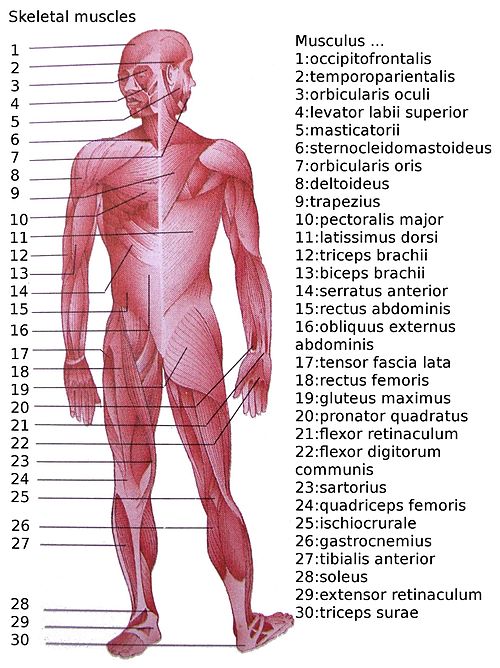
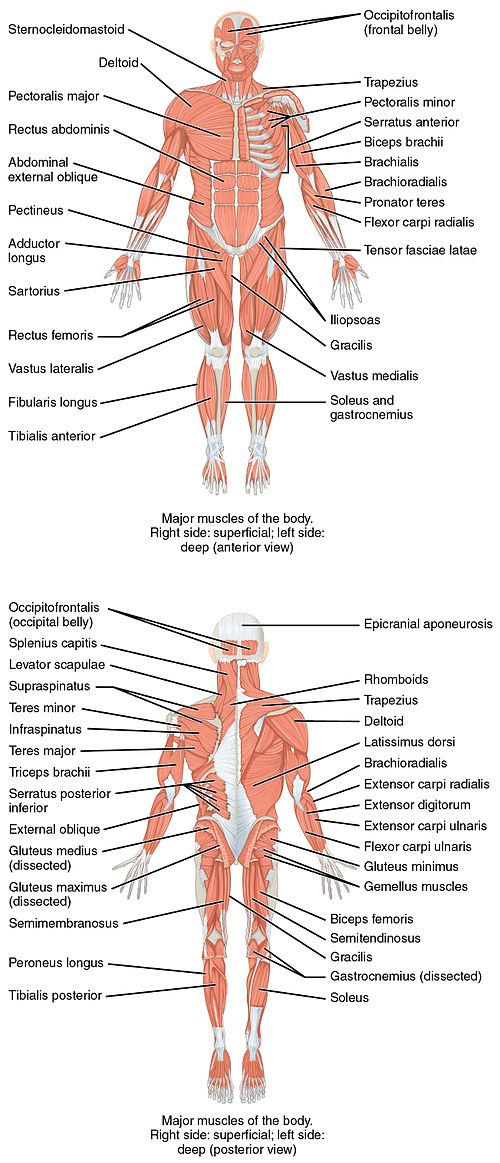
This is a table of skeletal muscles of the human beefcake.
There are around 650 skeletal muscles within the typical human being body.[1] [2] [iii] About every muscle constitutes one role of a pair of identical bilateral muscles, found on both sides, resulting in approximately 320 pairs of muscles, as presented in this article. Nevertheless, the exact number is difficult to define. Dissimilar sources group muscles differently, regarding what is defined as different parts of a single muscle or equally several muscles. At that place are also vestigial muscles that are present in some people only absent in others, such equally palmaris longus muscle.[four] [v]
The muscles of the human body can exist categorized into a number of groups which include muscles relating to the head and neck, muscles of the torso or trunk, muscles of the upper limbs, and muscles of the lower limbs.
The activeness refers to the action of each musculus from the standard anatomical position. In other positions, other deportment may be performed.
These muscles are described using anatomical terminology. The term "musculus" is omitted from muscle names (except when a musculus is an origin or insertion), and the term "bone" is omitted from bone names. The terms "artery" and "nerve" are both used when these structures are mentioned.
Head [edit]
Forehead/eyelid [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activeness | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| occipitofrontalis | two occipital bellies and 2 frontal bellies | epicranial aponeurosis | facial nervus [CNVII] | raises eyebrows | ||
| occipitalis | superior nuchal line of occipital bone, mastoid office of temporal bone | occipital avenue | posterior auricular nerve (facial nervus [CNVII]) | retracts scalp | ||
| frontalis | peel of eyebrow and glabella | ophthalmic artery | temporal branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | wrinkles eyebrow | ||
| orbicularis oculi | orbital part: frontal bone palpebral part: medial palpebral ligament lacrimal part: posterior crest of lacrimal os | orbital part: lateral palpebral raphe palpebral role: lateral palpebral raphe lacrimal part: Edges of eyelids | ophthalmic artery, zygomatico-orbital artery, athwart artery | zygomatic co-operative of facial nervus [CNVII] | closes eyelids | levator palpebrae superioris |
| corrugator supercilii | nasal part of frontal os | intermediate 3rd of skin of eyebrow | ophthalmic artery | zygomatic branch of facial nervus [CNVII] | moves skin of brow medially and inferiorly (towards root of nose) | |
| depressor supercilii | nasal office of frontal os, medial rim of orbit | medial third of skin of eyebrow | moves skin of eyebrows inferiorly |
[edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| levator palpebrae superioris | sphenoid bone | tarsal plate, upper eyelid | ophthalmic artery | oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | retracts and elevates eyelid | orbicularis oculi |
| superior tarsal | underside of levator palpebrae superioris | superior tarsal plate of eyelid | sympathetic nervous system | raises upper eyelid | ||
| Rectus muscles | ||||||
| superior | annulus of Zinn at orbital noon | 7.5 mm superior to corneal limbus | ophthalmic avenue | superior branch of oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | elevates, adducts, and medially rotates eye | |
| inferior | half dozen.5 mm inferior to corneal limbus | junior branch of oculomotor nervus [CNIII] | depresses and adducts eye | |||
| medial | 5.v mm medial to corneal limbus | inferior branch of oculomotor nerve [CNIII] | adducts eye | |||
| lateral | seven mm temporal to corneal limbus | abducens nerve [CNVI] | abducts heart | |||
| Oblique muscles | ||||||
| superior | annulus of Zinn at orbital apex, medial to optic culvert | outer posterior quadrant of eyeball | lateral muscular co-operative of ophthalmic artery | trochlear nerve [CNIV] | intorts, abducts, and depress heart | |
| inferior | orbital surface of maxilla, lateral to lacrimal groove | laterally onto eyeball, deep to lateral rectus, by a short apartment tendon | oculomotor nervus [CNIII] | extorts, elevates, and abducts centre | ||
Ear [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| temporoparietalis | auriculares muscles | epicranial aponeurosis | facial nerve [CNVII] | |||
| Auriculares | ||||||
| auricularis anterior | temporal fascia | front of helix of ear | posterior auricular artery | facial nerve [CNVII] | pulls auricle forwards | |
| auricularis superior | epicranial aponeurosis | dorsocranial surface of auricle | pulls auricle upwards | |||
| auricularis posterior | mastoid process of temporal os, tendon of sternocleidomastoid | dorsal part of auricle | pulls auricle backwards | |||
| Muscles of inner ear | ||||||
| stapedius | tip of pyramid of heart ear | cervix of stapes | stapedial co-operative of posterior auricular artery | facial nerve [CNVII] | reduces movement of stapes, controls amplitude of sound waves to inner ear | |
| tensor tympani | Eustachian tube | handle of malleus | superior tympanic artery | medial pterygoid nervus from mandibular nerve [CNV3] | tenses tympanic membrane, controls aamplitude of sound waves to inner ear | |
Olfactory organ [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| procerus muscle | fascia over lower part of nasal os | skin of lower part of forehead between eyebrows | facial artery | buccal branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | draws downward medial angle of eyebrow (giving expressions of frowning) | |
| depressor septi nasi | incisive fossa of maxilla | nasal septum and back part of alar part of nasalis | superior labial artery | depresses nasal septum | ||
| levator labii superioris alaeque nasi | frontal procedure of maxilla | nostril and upper lip | superior labial artery | dilates nostril, elevates upper lip, elevates wing of nose | ||
| nasalis | ||||||
| transverse role (compressor naris) | alveolar yoke of canine tooth | lateral nasal cartilage | superior labial avenue | buccal co-operative of facial nerve [CNVII] | compresses nostrils | |
| alar role (dilator naris) | alveolar yoke of lateral incisor tooth, greater and bottom alar cartilages | skin most margin of nostril | dilates nostrils | |||
Oral cavity [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| levator anguli oris (caninus) | maxilla | modiolus of oral cavity | facial artery | facial nervus [CNVII] | elevates angle of mouth (smiling) | |
| depressor anguli oris (triangularis) | tubercle of mandible | mandibular branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | depresses angle of oral fissure (frown) | |||
| levator labii superioris | medial part of infra-orbital margin of maxilla | skin and musculus of upper lip (labii superioris) | superior labial artery | buccal branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | elevates upper lip | |
| depressor labii inferioris | oblique line of mandible, betwixt symphysis and mental foramen | integument of lower lip, orbicularis oris fibers, its young man of opposite side | inferior labial avenue | mandibular branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | depresses lower lip | |
| mentalis | alveolar yoke of lower, lateral incisor tooth, found on anterior mandible | peel of chin | elevates and wrinkles skin of chin, protrudes lower lip | |||
| buccinator | alveolar processes of maxilla and mandible, pterygomandibular raphe | fibres of orbicularis oris | buccal avenue | buccal co-operative of facial nerve [CNVII] | compress cheeks against teeth (blowing), mastication | |
| orbicularis oris | maxilla and mandible | peel effectually lips | superior labial artery, inferior labial avenue | puckers lips | ||
| risorius | parotid fascia | modiolus of rima oris | facial artery | draw dorsum angle of rima oris | ||
| Zygomatic muscles | ||||||
| major | zygomatic os in region of zygomaticomaxillary suture | modiolus of mouth | facial artery | buccal branch of facial nerve [CNVII] | draws angle of mouth upwards and laterally | |
| small | skin of upper lip | elevates upper lip | ||||
Mastication [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nerve | Action | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| masseter | anterior 2-thirds of inferior margin of zygomatic arch and maxilla | angle of mandible, masseteric tuberosity of mandible | masseteric artery | masseteric nerve from mandibular nervus [CNV3] | elevates and retracts mandible (closes of oral cavity) | platysma |
| temporalis | temporal lines on parietal os of skull | coronoid process of mandible | deep temporal arteries | deep temporal nerves from mandibular nervus [CNV3] | ||
| Pterygoid muscles | ||||||
| lateral | greater wing of sphenoid and lateral pterygoid process | condyloid process of mandible | pterygoid branches of maxillary avenue | external pterygoid nerve from mandibular nerve [CNVthree] | depresses mandible | |
| medial | deep head : medial side of lateral pterygoid plate behind upper teeth superficial head : pyramidal process of palatine bone and maxillary tuberosity | medial angle of mandible | medial pterygoid nervus from mandibular nerve [CNV3] | elevates mandible, closes jaw, helps lateral pterygoid in moving jaw from side to side | ||
Tongue [edit]
Extrinsic musculus [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nervus | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| genioglossus | superior part of mental spine of mandible (symphysis menti) | dorsum of natural language, torso of hyoid | lingual avenue | hypoglossal nerve [CNXII] | inferior fibers: protrudes natural language middle fibers: depresses tongue superior fibers: draws tip of tongue dorsum and down | |
| hyoglossus | hyoid | side of tongue | depresses tongue | |||
| chondroglossus | bottom cornu and trunk of hyoid os | intrinsic muscular fibers of tongue | depresses tongue (some consider this muscle to be part of hyoglossus) | |||
| styloglossus | styloid process of temporal bone | tongue | sublingual co-operative of lingual artery | elevates and retracts tongue | junior and middle fibers of genioglossus | |
| palatoglossus | palatine aponeurosis | vagus nerve [CNX], accompaniment nerve [CNXI] | raising back role of tongue |
Intrinsic [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| superior longitudinal | close to epiglottis, from median gristly septum | edges of tongue | hypoglossal nerve [CNXII] | shortens tongue, turns tip upwardly, turns lateral margins upward | ||
| transversus | median fibrous septum | sides of tongue | narrows natural language with no elongation | |||
| junior longitudinal | root of natural language | apex of tongue | shortens tongue, retracts, pulls tip downward | |||
| verticalis | dorsum of tongue | inferior surface borders of tongue |
Soft palate [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tensor veli palatini | medial pterygoid plate of sphenoid os | palatine aponeurosis | medial pterygoid nerve from mandibular nervus [CNV3] | tenses soft palate, aids in swallowing | ||
| levator veli palatini | temporal bone, Eustachian tube | facial artery | pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve [CNX] | elevates soft palate | ||
| palatoglossus | palatine aponeurosis | tongue | aids in breathing by raising back function of tongue | |||
| palatopharyngeus | palatine aponeurosis and hard palate | upper border of thyroid cartilage (blends with constrictor fibers) | facial artery | pharyngeal branch of vagus nervus [CNX] | aids in breathing by pulling pharynx and larynx | |
| palatine uvula | hard palate | soft tissue of uvula | moves and changes shape of uvula |
Pharynx [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activeness | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stylopharyngeus | styloid process of temporal bone | thyroid cartilage (throat) | pharyngeal branches of ascending pharyngeal avenue | glossopharyngeal nerve [CNIX] | elevates larynx, elevates throat, swallowing | |
| salpingopharyngeus | cartilage of Eustachian tube | posterior fasciculus of pharyngopalatinus | vagus nervus [CNX], accompaniment nerve [CNXI] | raises nasopharynx | ||
| Pharyngeal muscles | ||||||
| inferior | cricoid cartilage, thyroid cartilage | pharyngeal raphe | pharyngeal branches of ascending pharyngeal artery | external laryngeal co-operative of superior laryngeal nerve from vagus nervus [CNX] | swallowing | |
| middle | hyoid bone | pharyngeal plexus of vagus nervus [CNX] | ||||
| superior | medial pterygoid plate, pterygomandibular raphé, alveolar process | pharyngeal raphe, pharyngeal tubercle | ||||
Larynx [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cricothyroid | anterior and lateral cricoid cartilage | inferior cornu and lamina of thyroid cartilage | cricothyroid branch of superior thyroid artery | external laryngeal branch of superior laryngeal nervus from vagus nerve [CNX] | tenses and elongates vocal folds (has minor adductory effect) | |
| arytenoid(transverse and oblique) | arytenoid cartilage on ane side | arytenoid cartilage on opposite side | superior laryngeal branch of superior thyroid avenue | recurrent laryngeal nerve from vagus nerve [CNX] | approximates arytenoid cartilages (closes rima glottidis) | |
| thyroarytenoid | inner (inductive) surface of thyroid cartilage | anterior surface of arytenoid cartilage | thickens and decreases length of vocal folds, adducts during speech | |||
| Cricoarytenoid muscles | ||||||
| posterior | posterior function of cricoid cartilage | muscular process of arytenoid cartilage | recurrent laryngeal nerve from vagus nerve [CNX] | abducts and laterally rotates cartilage, pulling vocal ligaments away from midline and forwards and and then opening rima glottidis | lateral cricoarytenoid | |
| lateral | lateral part of curvation of cricoid cartilage | adducts and medially rotates cartilage, pulling vocal ligaments towards midline and backwards and and so closing rima glottidis | posterior cricoarytenoid | |||
Neck [edit]
Clavicular [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| platysma | base of mandible | inferior clavicle and fascia of breast | branches of submental artery, branches of suprascapular artery | cervical co-operative of facial nerve [CNVII] | tenses skin of neck | masseter, temporalis |
| sternocleidomastoid | sternal head : manubrium sterni clavicular head : medial portion of clavicle | mastoid process of temporal os, superior nuchal line | occipital artery, superior thyroid avenue | motor: accessory nerve sensory: cervical plexus | acting alone: tilts head to its own side, rotates head and so face is turned towards reverse side acting together: flexes neck, raises sternum, assists in forced inspiration || |
Suprahyoid [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nervus | Action | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| digastric | anterior belly: digastric fossa (mandible) posterior belly : mastoid procedure of temporal bone | intermediate tendon (bottom horn of hyoid bone) | anterior belly: submental co-operative of facial artery posterior belly: occipital artery | inductive belly: mandibular nerve [CNV3] via mylohyoid nerve posterior belly: facial nerve [CNVII] | opens jaw when masseter and temporalis are relaxed | |
| stylohyoid | styloid process of temporal bone | greater horn of hyoid bone | occipital artery | facial nervus [CNVII] | elevates hyoid during swallowing | |
| mylohyoid | mylohyoid line of mandible | pharyngeal raphe | mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery | mylohyoid nervus, from inferior alveolar co-operative of mandibular nerve [CNV3] | raises oral cavity flooring, elevates hyoid, depresses mandible | |
| geniohyoid | mandibular symphysis | anterior surface of body of hyoid os | C1 via hypoglossal nerve | elevates hyoid and tongue upward during deglutition |
Infrahyoid [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sternohyoid | manubrium of sternum | hyoid os | superior thyroid avenue | ansa cervicalis | depresses hyoid | |
| sternothyroid | thyroid cartilage | depresses larynx, may slightly depress hyoid | ||||
| thyrohyoid | thyroid cartilage | hyoid bone | C1 | depress hyoid | ||
| omohyoid | upper border of scapula | junior thyroid avenue | ansa cervicalis | depresses larynx, depresses and moves to side hyoid |
Cervix [edit]
Inductive [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| longus colli | transverse processes of vertebrae C3, C4, C5, and C6 | inductive arch of atlas | C2, C3, C4, C5, C6 | flexes neck and head | ||
| longus capitis | anterior tubercles of transverse processes of vertebrae C3, C4, C5, and C6 | basilar function of occipital os | C1, C2, C3/C4 | flexes neck at atlanto-occipital articulation | ||
| rectus capitis anterior | atlas | occipital os | C1 | |||
| rectus capitis lateralis | upper surface of transverse procedure of atlas | nether surface of jugular process of occipital bone | sidebens at atlanto-occipital joint |
Lateral [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| scalene | cervical vertebrae | first and second ribs | ascending cervical artery (branch of inferior thyroid artery) | cervical nerves (C3, C4, C5, C6, C7) | elevates 1st and 2nd rib | |
| inductive | C3-C6 | first rib | ventral ramus of C5, C6 | when neck is fixed, elevates first rib to aid in animate or when rib is fixed, bends cervix forward and sideways and rotates it to opposite side | ||
| medius | C2-C6 | ventral rami of third to eighth cervical spinal nerves | elevates 1st rib, rotate cervix to reverse side | |||
| posterior | transverse processes of C4 – C6 | second rib | ascending cervical artery, superficial cervical avenue | C6, C7, C8 | elevates 2nd rib, tilts cervix to same side | |
| levator scapulae | posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 – C4 | superior part of medial border of scapula | dorsal scapular artery | cervical nerve (C3, C4) and dorsal scapular nerve (C5) | elevates scapula, tilts glenoid cavity inferiorly past rotating scapula | serratus anterior |
| rectus capitis lateralis | upper surface of transverse procedure of atlas (C1) | under surface of jugular process of occipital os | C1 | |||
| obliquus capitis superior | lateral mass of atlas | lateral half of inferior nuchal line | suboccipital nerve | |||
| obliquus capitis inferior | barbed process of axis | lateral mass of atlas | suboccipital nervus |
Posterior [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rectus capitis posterior minor | tubercle on posterior curvation of atlas (C1) | medial office of inferior nuchal line of occipital bone and surface between it and foramen magnum | a branch of dorsal master division of suboccipital nerve | extends caput at neck, but is now considered to exist more than of a sensory organ than a muscle | ||
| rectus capitis posterior major | barbed process of axis (C2) | inferior nucheal line of occipital bone | dorsal ramus of C1 (suboccipital nerve) | |||
| semispinalis capitis | articular processes of C4-C6; transverse processes of C7 and T1-T7 | occipital bone between superior and junior nuchal lines | greater occipital nervus | extends head | ||
| longissimus capitis | articular processes of C4-C7; transverse processes of T1-T5 | posterior margin of mastoid process | lateral sacral artery | posterior branch of spinal nerve | laterally: Flexes caput and neck to same side. bilaterally: Extend vertebral column || | |
| splenius capitis | ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of C7-T6 | mastoid process | C3, C4 | extends, rotates, and laterally flex head | ||
| obliquus capitis superior | lateral mass of atlas | lateral half of inferior nuchal line | suboccipital nerve | |||
| obliquus capitis junior | spinous process of centrality | lateral mass of atlas |
Torso [edit]
Dorsum [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Action | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| erector spinae | spines of last four thoracic vertebrae | both spines of nearly cranial thoracic vertebrae and cervical vertebrae | lateral sacral artery | posterior branch of spinal nerve | extends vertebral column | rectus abdominis |
| iliocostalis | ||||||
| longissimus | transverse process | transverse process | ||||
| spinalis | spinous process | spinous process | ||||
| latissimus dorsi | spinous processes of thoracic T6-T12, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and inferior three or iv ribs | floor of intertubercular groove of humerus | subscapular avenue, dorsal scapular artery | thoracodorsal nerve | pulls forelimb dorsally and caudally | deltoid, trapezius |
| transversospinales | transverse process | spinous process | posterior branches of spinal nerve | |||
| semispinalis thoracis (dorsi) | transverse processes of sixth to tenth thoracic vertebrae | spinous processes of upper iv thoracic vertebrae and lower two cervical vertebrae | ||||
| semispinalis cervicis (colli) | transverse processes of upper v or half-dozen thoracic vertebrae | cervical spinous processes, from centrality to fifth | ||||
| semispinalis capitis (complexus) | transversal procedure of lower cervical and higher thoracal columna | surface area between superior and junior nuchal line | greater occipital nerve | extends head | ||
| multifidus | sacrum, erector spinae aponeurosis, PSIS, and iliac crest | spinous process | posterior branch of spinal nervus | stabilizes vertebrae in local movements of vertebral column | ||
| rotatores | transverse procedure | posterior branch | ||||
| interspinales | barbed process | posterior rami of spinal nerves | extends, flexes, and rotates vertebral column | |||
| intertransversarii | transverse process | transverse process higher up | laterally flexes trunk | |||
| splenius | ||||||
| capitis | nuchal ligament, spinous process of C7-T6 | mastoid process of temporal bone, occipital bone | C3, C4 | extends, rotates, and laterally flexes head | ||
| cervicis | spinous processes of T3-T6 | transverse processes of C1, C2, C3 | C5, C6 | |||
Breast [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| intercostals | ribs 1–11 | ribs 2–12 | intercostal arteries | intercostal fretfulness | ||
| external | inhalation | internal | ||||
| internal | rib – inferior border | rib – superior border | holds ribs steady | external | ||
| innermost | elevates ribs | |||||
| subcostales | inner surface of one rib | inner surface of 2d or third rib in a higher place, virtually its bending | ||||
| transversus thoracis | costal cartilages of terminal three–4 ribs, body of sternum, xiphoid process | ribs/costal cartilages 2–6 | depresses ribs | |||
| levatores costarum | transverse processes of C7 to T12 vertebrae | superior surfaces of ribs immediately inferior to preceding vertebrae | dorsal rami – C8, T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11 | assists in elevation of thoracic rib cage | ||
| Serratus posterior muscles | ||||||
| inferior | vertebrae T11 – L3 | inferior borders of 9th through 12th ribs | intercostal arteries | intercostal nerves | depresses lower ribs, aiding in expiration | |
| superior | nuchal ligament (or ligamentum nuchae) and spinous processes of vertebrae C7 through T3 | upper borders of 2nd through 5th ribs | 2nd through 5th intercostal fretfulness | elevates ribs, aiding in inspiration | ||
| diaphragm | pericardiacophrenic artery, musculophrenic artery, junior phrenic arteries | phrenic and lower intercostal fretfulness | breathing | |||
Pelvis [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activeness | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coccygeus | sacrospinous ligament | coccyx | sacral nerves: S4, S5 or S3-S4 | closes back part of pelvic outlet | ||
| Levator ani | ||||||
| iliococcygeus | ischial spine, posterior office of tendinous arch of pelvic fascia | coccyx and anococcygeal raphe | inferior gluteal artery | levator ani nerve (S4)
| supports organs in pelvic cavity | |
| pubococcygeus | back surface of pubis, anterior part of obturator fascia | coccyx and sacrum | controls urine menstruation, contracts during orgasm | |||
| puborectalis | lower part of pubic symphysis | - | S3, S4. levator ani nerve | inhibits defecation | ||
Perineum [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphincter ani | ||||||
| externus | - | - | junior rectal artery | S4 and twigs from inferior anal nerves of pudendal nerve | keeps anal canal and anus closed, aids in expulsion of carrion | |
| internus | - | - | pudendal nerve | |||
| Superficial perineal pouch | ||||||
| transversus perinei superficialis | anterior surface of ischial tuberosity | central point of perineum | perineal avenue | pudendal nerve | ||
| bulbospongiosus | perineal raphe | - | empties urethra (men) clenches vagina (women) || | |||
| ischiocavernosus | ischial tuberosity | crus of penis (men) crus of clitoris (women) | assists bulbospongiosus | |||
| Deep perineal pouch | ||||||
| transversus perinei profundus | inferior ramus of ischium | its young man of opposite side | pudendal nerve | |||
| sphincter urethrae membranaceae | junction of inferior rami of pubis and ischium near one.25 – 2 cm, and from neighboring fascia | perineal branch of pudendal nerve (S2, S3, S4) | constricts urethra, maintains urinary continence | |||
Upper limb [edit]
Vertebral column [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trapezius | down midline, external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament, medial part of superior nuchal line, spinous processes of vertebrae C7-T12 | at shoulders, lateral third of clavicle, acromion of scapula, spine of scapula | transverse cervical artery | motor: accessory nerve [CNXI] sensory: cervical nerves C3 and C4 | retracts and elevates scapula | serratus anterior |
| latissimus dorsi | spinous processes of thoracic T6-T12, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and inferior 3 or 4 ribs | floor of intertubercular groove of humerus | subscapular avenue, dorsal scapular artery | thoracodorsal nerve | pulls forelimb dorsally and caudally | deltoid, trapezius |
| rhomboids | nuchal ligaments, barbed processes of C7-T5 vertebrae | medial edge of scapula | dorsal scapular artery | dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5) | retracts scapula and rotates information technology to depress glenoid cavity, fixes scapula to thoracic wall | serratus inductive |
| rhomboid major | spinous processes of T2 to T5 vertebrae | medial border of scapula, inferior to insertion of rhomboid small-scale | ||||
| rhomboid minor | nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7- to T1 vertebrae | medial border of scapula, superior to insertion of rhomboid major | ||||
| levator scapulae | posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 – C4 vertebrae | superior part of medial border of scapula | cervical nerve (C3, C4) and dorsal scapular nerve (C5) | elevates scapula, tilts glenoid cavity inferiorly past rotating scapula |
Thoracic walls [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Activeness | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pectoralis major | clavicular head: anterior surface of medial one-half of clavicle sternocostal head: anterior surface of sternum, superior six costal cartilages | intertubercular groove of humerus | pectoral co-operative of thoracoacromial artery | lateral pectoral nerve, medial pectoral nervus clavicular head: C5 and C6 sternocostal head: C7, C8 and T1 | adducts and medially rotates humerus, draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly clavicular head: flexes humerus sternocostal head: extends humerus | |
| pectoralis minor | tertiary to 5th ribs, nigh their costal cartilages | medial edge and superior surface of coracoid process of scapula | medial pectoral nerve (C8, T1) | stabilizes scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against thoracic wall | ||
| subclavius | first rib | subclavian groove of clavicle | thoracoacromial artery, clavicular branch | subclavian nerve | depresses clavicle | |
| serratus inductive | fleshy slips from outer surface of upper 8 or 9 ribs | costal surface of medial margin of scapula | upper part: lateral thoracic artery lower part:thoracodorsal artery | long thoracic nerve (from roots of brachial plexus C5, C6, C7) | protracts and stabilises scapula, assists in upward rotation | rhomboid major, rhomboid pocket-sized, trapezius |
Shoulder [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| deltoid | clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula | deltoid tuberosity of humerus | primarily posterior circumflex humeral avenue | axillary nerve | abducts, flexes, and extends shoulder | latissimus dorsi |
| teres major | posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula | medial lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus | subscapular avenue, circumflex scapular artery | lower subscapular nerve (segmental levels C5 and C6) | internally rotates humerus | |
| Rotator cuff | ||||||
| supraspinatus | supraspinous fossa of scapula | superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus | suprascapular artery | suprascapular nerve | abducts and stabilises humerus | infraspinatus, teres minor, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi |
| infraspinatus | infraspinous fossa of scapula | middle facet of greater tubercle of humerus | suprascapular avenue, circumflex scapular artery | laterally rotates, adducts, and stabilises humerus | subscapularis, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi | |
| teres pocket-sized | lateral border of scapula | inferior facet of greater tubercle of humerus | posterior circumflex humeral artery, circumflex scapular artery | axillary nervus | laterally rotates and adducts humerus | subscapularis, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi |
| subscapularis | subscapular fossa of scapula | bottom tubercle of humerus | subscapular artery | upper subscapular nervus, lower subscapular nerve (C5, C6) | medially rotates humerus, stabilizes shoulder | infraspinatus, teres minor |
Arm [edit]
Anterior compartment [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coracobrachialis | coracoid process of scapula | medial surface of humerus | brachial artery | musculocutaneous nerve | flexes and adducts shoulder | |
| biceps brachii | brusque head: coracoid process of scapula long head: supraglenoid tubercle | radial tuberosity, bicipital aponeurosis | musculocutaneous nervus (lateral cord: C5, C6, C7) | flexes elbow, supinates forearm | triceps brachii | |
| brachialis | inductive surface of humerus (mainly distal half) | coronoid process of ulna, tuberosity of ulna | radial recurrent artery | musculocutaneous nerve | flexes elbow |
Posterior compartment [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| triceps brachii | long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula lateral head: posterior humerus (above radial sulcus) medial caput: posterior humerus - (below radial sulcus) | olecranon of ulna | deep artery of arm | radial nerve | extends forearm long head: adducts shoulder medial head: does non function at shoulder | biceps brachii, brachialis |
| anconeus | lateral epicondyle of humerus | lateral surface of olecranon, superior part of posterior ulna | deep artery of arm, interosseous recurrent avenue | radial nerve (C7, C8, and T1) | partly blended with triceps, extendsforearm, stabilises elbow, abducts ulna during pronation |
Forearm [edit]
Inductive compartment [edit]
Superficial [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nerve | Activity | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pronator teres | humeral head: medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon) ulnar head: coronoid process of ulna | pronator tuberosity of radius | ulnar avenue, radial avenue | median nervus | pronates forearm, flexes elbow | supinator |
| flexor carpi radialis | medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon) | bases of 2nd metacarpal, base of 3rd metacarpal | radial artery | flexes and abducts wrist | extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi radialis longus | |
| palmaris longus | palmar aponeurosis | ulnar artery | flexes wrist | extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi ulnaris | ||
| flexor carpi ulnaris | pisiform, hook of hamate, base of operations of 5th metacarpal | muscular branches of ulnar nervus | flexes and adducts wrist | extensor carpi ulnaris | ||
| flexor digitorum superficialis | medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon), parts of radius and ulna | bases of eye phalanges 2, 3, iv, and five | median nerve | flexes fingers (primarily at proximal interphalangeal joints) | extensor digitorum |
Deep [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activeness | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pronator quadratus | medial anterior surface of ulna | lateral inductive surface of radius | inductive interosseous artery | inductive interosseous nerve (median nerve) | weakly pronates forearm | supinator |
| flexor digitorum profundus | ulna | distal phalanges | lateral belly: anterior interosseous nerve (median nerve) medial belly: muscular branches of ulna nerve | flexes wrist, flexes interphalangeal joints | extensor digitorum | |
| flexor pollicis longus | middle half of volar surface of radius, interosseus membrane | base of distal phalanx of thumb | anterior interosseous nervus (median nervus) (C8, T1) | flexes pollex | extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis |
Posterior compartment [edit]
Superficial [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| extensor digitorum | lateral epicondyle of humerus (common extensor tendon) | 2nd–5th phalanges | posterior interosseous artery | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | extends hand, extends fingers | flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus |
| extensor digiti minimi | inductive surface of lateral epicondyle of humerus (common extensor tendon) | extensor expansion, located at base of proximal phalanx on dorsal side | extends pinkie at all joints | flexor digiti minimi brevis | ||
| extensor carpi ulnaris | lateral epicondyle of humerus (common extensor tendon), ulna | 5th metacarpal | ulnar artery | extends and adducts wrist | flexor carpi ulnaris | |
| Mobile wad | ||||||
| brachioradialis | lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus | radial styloid procedure (distal radius) | radial recurrent artery | radial nervus | flexes forearm, pronates forearm when supine, supinates forearm when prone | |
| extensor carpi radialis longus | 2nd metacarpal | radial artery | extends wrist joint, abducts paw at wrist | flexor carpi radialis | ||
| extensor carpi radialis brevis | anterior surface of lateral epicondyle of humerus (common extensor tendon) | base of third metacarpal | posterior interosseus nervus | |||
Deep [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| supinator | lateral epicondyle of humerus, supinator crest of ulna, radial collateral ligament, annular ligament | lateral proximal shaft of radius | radial recurrent artery | posterior interosseus nerve (C7, C8) | supinates forearm | pronator teres, pronator quadratus |
| extensor indicis | ulna | index finger (extensor hood) | extends index finger, wrist | |||
| Anatomical snuff box | ||||||
| abductor pollicis longus | ulna | offset metacarpal | posterior interosseous avenue | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | abducts and extends thumb | adductor pollicis |
| extensor pollicis brevis | radius, interosseous membrane of forearm | proximal phalanx of pollex | extends thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint | flexor pollicis longus, flexor pollicis brevis | ||
| extensor pollicis longus | ulna, interosseous membrane of forearm | distal phalanx of thumb | extends pollex (metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal) | |||
Paw [edit]
Lateral volar [edit]
Thenar [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activeness | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| opponens pollicis | trapezium, transverse carpal ligament | metacarpal bone of thumb on its radial side | superficial palmar arch | median nerve | opposes pollex | |
| flexor pollicis brevis | trapezoid, flexor retinaculum | thumb, proximal phalanx | median nerve, deep branch of ulnar nerve (medial head) | flexes pollex | extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis | |
| abductor pollicis brevis | flexor retinaculum of hand, scaphoid and trapezium | radial base of proximal phalanx of thumb and thumb extensors | median nerve | abducts thumb | adductor pollicis | |
| adductor pollicis | transverse head: anterior trunk of third metacarpal oblique head: bases of second and 3rd metacarpals and side by side trapezoid and capitate bones | medial side of base of operations of proximal phalanx of pollex and ulnar sesamoid | deep palmar arch | deep branch of ulnar nervus (T1) | adducts thumb at carpometacarpal joint | abductor pollicis longus, abductor pollicis brevis |
Medial volar [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activeness | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| palmaris brevis | flexor retinaculum (medial), palmar aponeurosis | palm | palmar metacarpal artery | superficial branch of ulnar nervus | contraction skin of palm | |
| hypothenar | ||||||
| abductor digiti minimi | pisiform | base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit on ulnar or medial side | ulnar artery | deep branch of ulnar nerve | abducts little finger | |
| flexor digiti minimi brevis | hamate bone | little finger | deep co-operative of ulnar nervus | flexes pinkie | extensor digiti minimi | |
| opponens digiti minimi | claw of hamate, flexor retinaculum | medial border of fifth metacarpal | deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) | draws 5th metacarpal anteriorly and rotates it, bringing little finger (5th digit) into opposition with pollex | ||
Intermediate [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lumbrical | flexor digitorum profundus | extensor expansion | superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital arteries, deep palmar arch, dorsal digital artery | deep co-operative of ulnar nerve, median nervus | flex metacarpophalangeal joints, extend interphalangeal joints | |
| dorsal interossei | metacarpals | proximal phalanges | dorsal metacarpal artery, palmar metacarpal artery | deep co-operative of ulnar nerve | abduct fingers | palmar interossei |
| palmar interossei | palmar metacarpal artery | adduct fingers | dorsal interossei |
Lower limb [edit]
Iliac region [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iliopsoas | iliac fossa (iliacus), sacrum (iliacus), spine (T12, L1, lumbar vertebra, psoas major, psoas minor)[6] | lesser trochanter of femur (psoas major), shaft below bottom trochanter (iliacus), tendon of psoas major & femur (iliacus)[6] | medial femoral circumflex artery, iliolumbar artery | femoral nerve, lumbar nerves L1, L2 | flexes hip (psoas major/minor, iliacus), spine rotation (psoas major/pocket-sized) | gluteus maximus, posterior compartment of thigh |
| psoas major | transverse processes, bodies and intervertebral discs of T12-L5 vertebrae | lesser trochanter of femur | iliolumbar artery | lumbar plexus via anterior branches of L1, L2, L3[vii] | flexes and rotates laterally thigh | gluteus maximus |
| psoas minor | side of T11+L1 and IV intervertebral disc | Pectineal line and iliopectineal eminence | iliolumbar avenue, lumbar arteries | L1 | weakly flexes body flexor | |
| iliacus | iliac fossa | lesser trochanter of femur | medial femoral circumflex artery, Iliolumbar artery | femoral nervus (L2, L3[7]) | flexes hip[eight] |
Gluteal [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tensor fasciae latae | iliac crest | iliotibial tract | primarily lateral circumflex femoral artery, superior gluteal avenue | superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5) | flexes thigh, medially rotates thigh, stabilises torso | |
| gluteal | ||||||
| gluteus maximus | gluteal surface of ilium, lumbar fascia, sacrum, sacrotuberous ligament | gluteal tuberosity of femur, iliotibial tract | superior gluteal artery, inferior gluteal artery | junior gluteal nervus (L5, S1, S2 nerve roots) | externally rotates and extends hip joint, supports extended genu through iliotibial tract, chief antigravity muscle in sitting | Iliacus, psoas major, psoas pocket-size |
| gluteus medius | gluteal surface of ilium, under gluteus maximus | greater trochanter of femur | superior gluteal avenue | superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1 nervus roots) | abduction of hip; preventing adduction of hip Medial rotation of thigh | lateral rotator group |
| gluteus minimus | gluteal surface of ilium, under gluteus medius | |||||
| lateral rotator group | at or below acetabulum of ilium | on or most greater trochanter of femur | inferior gluteal artery, lateral sacral artery, superior gluteal avenue | obturator nerve, piriformis nervus, nerve to quadratus femoris | laterally rotates hip | gluteus minimus, gluteus medius |
| piriformis | sacrum | greater trochanter | piriformis nervus (S1 and S2 nerve roots)[9] | laterally rotates (outward) thigh | ||
| obturator externus | obturator foramen and obturatory membrane | medial surface of greater trochanter of femur | obturator avenue | posterior branch of obturator nerve (L3, L4) | adduct thigh, rotate laterally thigh | |
| superior gemellus | ischial spine | nerve to obturator internus (L5, S1, S2) | ||||
| obturator internus | ischiopubic ramus, obturator membrane | medial surface of greater trochanter of femur | abducts & rotates laterally thigh, stabilises hip during walking | |||
| inferior gemellus | ischial tuberosity | obturator internus tendon | nerve to quadratus femoris (L4, L5, S1) | laterally rotates thigh | ||
| quadratus femoris | intertrochanteric crest | inferior gluteal avenue | ||||
Thigh [edit]
Anterior compartment [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nervus | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| articularis genus | femur | suprapatellar bursa | femoral artery | femoral nerve | pulls suprapatellar bursa during extension of genu | |
| sartorius | superior to anterior superior iliac spine | medial side of upper tibia in pes anserinus | flexes, laterally rotates, and abducts thigh, flexes and medially rotates leg | |||
| quadriceps femoris | combined rectus femoris and vastus muscles | patella and tibial tuberosity via patellar tendon | extends knee, flexes hip (rectus femoris only) | hamstring | ||
| rectus femoris | anterior inferior iliac spine and outside surface of bony ridge which forms iliac portion of acetabulum | articulatio genus extension; hip flexion | ||||
| vastus lateralis | greater trochanter, intertrochanteric line, and linea aspera of femur | extends knee | ||||
| vastus intermedius | anterior surface of femur | |||||
| vastus medialis | anteromedial surface of femur |
Posterior compartment/hamstring [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activeness | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hamstring | quadriceps femoris | |||||
| biceps femoris | long caput: ischial tuberosity short head: linea aspera of femur[x] | head of fibula[10] articulating with back of lateral tibial condyle | inferior gluteal artery, perforating arteries, popliteal artery | long head: medial (tibial) part of sciatic nervus short head: lateral (mutual fibular) part of sciatic nervus[10] | flexes articulatio genus, laterally rotates leg at knee joint (when knee is flexed), extends hip joint (long head only)[x] | |
| semitendinosus | ischial tuberosity[10] | pes anserinus | inferior gluteal artery, perforating arteries | sciatic nerve[10] (tibial, L5, S1, S2) | flexes genu, extends hip, medially rotates leg at genu[10] | |
| semimembranosus | medial surface of tibia[10] | profunda femoris, gluteal artery | sciatic nerve[10] |
Medial compartment [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nerve | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| adductor muscles of the hip | pubis | femur, tibia | obturator artery | obturator nervus | adducts hip | gluteus medius, gluteus minimus |
| gracilis | inferior pubic ramus[11] | tibia (pes anserinus) | inductive branch of obturator nervus[xi] | adducts hip, flexes hip, medially rotates knee[eleven] | ||
| pectineus | superior pubic ramus[xi] | bottom trochanter, linea aspera | femoral nerve and obturator nerve (medial compartment)[11] | flexes and adducts hip[11] | ||
| adductor brevis | anterior surface of inferior pubic ramus[11] | lesser trochanter and linea aspera of femur | anterior branch of obturator nerve[eleven] | adducts hip[11] | ||
| adductor longus | pubic body just beneath pubic crest | centre third of linea aspera | adducts and medially rotates hip[11] | |||
| adductor magnus | [11] | femur, adductor tubercle of femur | posterior branch of obturator nerve (adductor) and tibial role of sciatic nerve (vertical head)[11] [12] | adducts hip[11] |
Leg [edit]
Anterior compartment [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nervus | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tibialis anterior | torso of tibia | medial cuneiform and first metatarsal basic of foot | anterior tibial avenue | deep fibular nerve | dorsiflexes and inverts foot | fibularis longus, gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, tibialis posterior |
| extensor hallucis longus | middle portion of anterior surface of fibula, inductive surface of interosseous membrane | dorsal side of base of distal phalanx of hallux | extends big toe, assists in dorsiflexion of pes at ankle, weakly inverts human foot | flexor hallucis longus, flexor hallucis brevis | ||
| extensor digitorum longus | lateral condyle of tibia, superior ¾ of interosseous membrane | middle and distal phalanges of lateral four digits | extension of toes and talocrural joint | flexor digitorum longus, flexor digitorum brevis | ||
| fibularis tertius | distal anterior surface of fibula | dorsal surface of fifth metatarsal | dorsi flexes and everts foot |
Posterior compartment [edit]
Superficial [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activity | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| triceps surae | achilles tendon, calcaneus | posterior tibial avenue | tibial nerve | plantarflexes talocrural joint | ||
| gastrocnemius | medial condyle and lateral condyle of femur | calcaneus | sural arteries | tibial nerve from sciatic nerve, specifically, nerve roots S1, S2 | plantarflexes ankle, flexes human knee (minor) | tibialis inductive |
| soleus | fibula, medial border of tibia (soleal line) | tendo calcaneus | tibial nerve, specifically, nerve roots 505–Southward2 | plantarflexes ankle | ||
| plantaris | lateral supracondylar ridge of femur above lateral head of gastrocnemius | calcaneal tendon (medial side, deep to gastrocnemius tendon) | tibial nerve | plantarflexes talocrural joint, flexes human knee |
Deep [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| popliteus | middle facet of lateral surface of lateral femoral condyle | posterior tibia under tibial condyles | popliteal avenue | tibial nervus | medially rotates and flexes knee | |
| tarsal tunnel | ||||||
| flexor hallucis longus | posterior surface of upper 1/3 of fibula | base of distal phalanx of hallux | fibular artery (peroneal branch of posterior tibial artery | tibial nervus, S1, S2 nerve roots | flexes all joints of big toe, plantarflexes talocrural joint | extensor hallucis longus |
| flexor digitorum longus | medial tibia | distal phalanges of lateral four digits | posterior tibial avenue | tibial nervus | flexes toes | extensor digitorum longus, extensor digitorum brevis |
| tibialis posterior | tibia, fibula | navicular, medial cuneiform | inverts foot, plantarflexes foot at ankle | tibialis anterior | ||
Lateral compartment [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fibularis longus | fibula | first metatarsal, medial cuneiform | fibular artery | superficial fibular nervus | plantarflexes and everts ankle | tibialis anterior |
| fibularis brevis | fibula | fifth metatarsal | fibular artery | superficial fibular nerve | plantarflexes and everts ankle | tibialis posterior |
Foot [edit]
Dorsal [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Activeness | Adversary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| extensor digitorum brevis | calcaneus | toes | deep fibular nerve | extends digits 2, 3, and 4 | flexor digitorum longus, flexor digitorum brevis | |
| extensor hallucis brevis | base of proximal phalanx of big toe | deep fibular nerve | extends big toe | flexor hallucis brevis | ||
| dorsal interossei of human foot | metatarsals | proximal phalanges | lateral plantar nerve(4th interosseous space: superficial branch others: deep branch), beginning and 2d interossei: lateral co-operative of deep fibular nerve | abducts toes | plantar interossei |
Plantar [edit]
Get-go layer [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Avenue | Nervus | Activity | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abductor hallucis | medial procedure of calcaneus, flexor retinaculum, plantar aponeurosis | medial side of base of proximal phalanx of start digit | medial plantar nervus | abducts hallux | adductor hallucis | |
| flexor digitorum brevis | medial process of calcaneus, plantar aponeurosis, intermuscular septa | centre phalanges of digits 2–v | flexes lateral four toes | extensor digitorum longus, extensor digitorum brevis | ||
| abductor digiti minimi | plantar aponeurosis | phalanges of 5th toe | lateral plantar avenue | lateral plantar nerve (S1, S2) | flexes and abducts fifth toe | flexor digiti minimi brevis |
2d layer [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| quadratus plantae | calcaneus | tendons of flexor digitorum longus | lateral plantar nerve (S1, S2) | flexes distal interphalangeal joints (assists flexor digitorum longus) | ||
| lumbricals | tendons of flexor digitorum longus | medial surface of extensor expansion of proximal phalanges of lateral four toes | lateral plantar artery, plantar arch, 4 plantar metatarsal arteries | lateral plantar nerve (lateral three lumbricals) and medial plantar nerve (first lumbrical) | maintain extension of digits at interphalangeal joints |
3rd layer [edit]
| Musculus | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| flexor hallucis brevis | plantar surface of cuneiforms, plantar calcaneocuboid ligament, long plantar ligament | medial head: medial sesamoid os of metatarsophalangeal articulation, proximal phalanx of peachy toe lateral caput: lateral sesamoid bone of metatarsophalangeal joint, proximal phalanx of slap-up toe | medial plantar nerve | flexes big toe | extensor hallucis longus | |
| adductor hallucis | oblique head: proximal ends of middle 3 metatarsals transverse head: metatarsophalangeal joints, ligaments of lateral three toes | lateral side of base of operations of proximal phalanx of big toe, sesamoid | lateral plantar nerve | adducts big toe | abductor hallucis | |
| flexor digiti minimi brevis | fifth metatarsal bone | phalanx of fifth toe | lateral plantar nerve (superficial co-operative) | extends and adducts fifth toe | abductor digiti minimi |
4th layer [edit]
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nervus | Action | Antagonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plantar interossei | tendons of plantar Interossei | proximal phalanges 3-V - muscles cantankerous the metatarsophalangeal joint of toes Three-V and so the insertions correspond with the origin and at that place is no crossing between toes | plantar arch, dorsal metatarsal artery | lateral plantar nerve | adducts toes three - five, strengthens transverse curvation | dorsal interossei |
| dorsal interossei | metatarsals | proximal phalanges | lateral plantar nerve | abducts toes | plantar interossei |
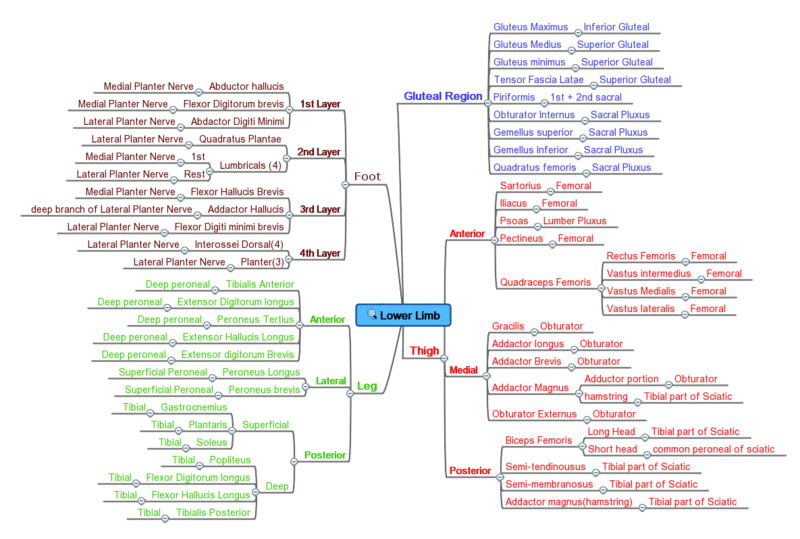
Innervation overview [edit]

Mind Map showing a summary of Upper Limb Muscle Innervation
See besides [edit]
- Accessory muscle
- List of bones of the human skeleton
- List of nerves of the human being body
- Circulatory system
- Blood vessel
References [edit]
- ^ Science Reference Department (19 November 2019). "What is the strongest muscle in the human body?". Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. 20540 Usa. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2021-05-01 .
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Brooks, Susan V. (2003-12-01). "Current topics for education skeletal muscle physiology". Advances in Physiology Instruction. 27 (1–4): 171–182. doi:10.1152/advan.00025.2003. ISSN 1043-4046. PMID 14627615.
- ^ John., Stewart, Gregory (2009). "Chapter eight: Skeletal muscles". The skeletal and muscular systems. New York: Chelsea Business firm. ISBN9781604133653. OCLC 277118444.
- ^ de las Peñas, César Fernández; Ge, Hong-Yous; Arendt-Nielsen, Lars; Dommerholt, Jan; Simons, David G. (2011). "Affiliate 32 - Referred pain from muscle/myofascial trigger points". Neck and Arm Pain Syndromes. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 404–418. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-3528-9.00032-seven. ISBN978-0-7020-3528-9.
- ^ Sarnat, Harvey B.; Carpenter, Stirling (2015). "Chapter 4 - Musculus Biopsy for Diagnosis of Neuromuscular and Metabolic Diseases". Neuromuscular Disorders of Infancy, Childhood, and Adolescence (2nd ed.). Bookish Press. pp. 46–65. ISBN978-0-12-417044-5.
- ^ a b "Iliopsoas". exrx.net.
- ^ a b Essential Clinical Beefcake. K.Fifty. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Folio 193
- ^ Gosling, J. A., Harris, P. F., Humpherson, J. R., Whitmore I., & Willan P. L. T. 2008. Human being Anatomy Color Atlas and Text Book. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier. page 200
- ^ Essential Clinical Beefcake. One thousand.Fifty. Moore & A.1000. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Page 217
- ^ a b c d due east f g h i Gosling 2008, p. 273
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j one thousand 50 thou Gosling et al. 2008, p. 266
- ^ MedicalMnemonics.com: 255 [ dead link ]
External links [edit]
- LUMEN's Master Muscle List
- PT Central - Consummate Muscle Tables for the Human being Trunk
- Lower Extremity Musculus Atlas
- Tutorial and quizzes on skeletal muscular anatomy
- Muscles of man body (too hither)
- Beefcake quiz
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_skeletal_muscles_of_the_human_body
0 Response to "Side Man Body Drawing Muscle"
Postar um comentário